The origin of p-type conductivity in ZnM2O4 (M = Co, Rh, Ir) spinels
Abstract
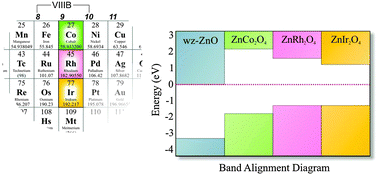
ZnM2O4 (M = Co, Rh, Ir) spinels are considered as a class of potential p-type transparent conducting oxides (TCOs). We report the formation energy of acceptor-like defects using first principles calculations with an advanced hybrid exchange–correlation functional (HSE06) within density functional theory (DFT). Due to the discrepancies between the theoretically obtained band gaps with this hybrid functional and the – scattered – experimental results, we also perform GW calculations to support the validity of the description of these spinels with the HSE06 functional. The considered defects are the cation vacancy and antisite defects, which are supposed to be the leading source of disorder in the spinel structures. We also discuss the band alignments in these spinels. The calculated formation energies indicate that the antisite defects ZnM (Zn replacing M, M = Co, Rh, Ir) and VZn act as shallow acceptors in ZnCo2O4, ZnRh2O4 and ZnIr2O4, which explains the experimentally observed p-type conductivity in those systems. Moreover, our systematic study indicates that the ZnIr antisite defect has the lowest formation energy in the group and it corroborates the highest p-type conductivity reported for ZnIr2O4 among the group of ZnM2O4 spinels. To gain further insight into factors affecting the p-type conductivity, we have also investigated the formation of localized small polarons by calculating the self-trapping energy of the holes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...