Marked enhancement in electron–hole separation achieved in the low bias region using electrochemically prepared Mo-doped BiVO4 photoanodes†
Abstract
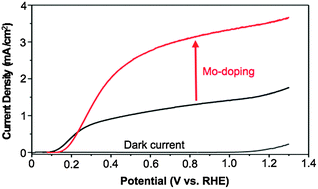
Mo-doped BiVO4 electrodes were prepared by an electrochemical route for use as photoanodes in a photoelectrochemical cell. The purpose of Mo-doping was to improve the electron transport properties, which in turn can increase the electron–hole separation yield. The poor electron–hole separation yield was known to be one of the main limiting factors for BiVO4-based photoanodes. The electrochemical route provided an effective way of doping BiVO4, and the optimally doped sample, BiV0.97Mo0.03O4, increased the electron–hole separation yield from 0.23 to 0.57 at 0.6 V vs. RHE, which is a record high separation yield achieved for BiVO4-based photoanodes. As a result, BiV0.97Mo0.03O4 generated impressive photocurrents, for example, 2 mA cm−2 at a potential as low as 0.4 V vs. RHE for sulfite oxidation, which has fast oxidation kinetics and, therefore, the loss of holes by surface recombination is negligible. For photooxidation of water, BiV0.97Mo0.03O4 was paired with FeOOH as an oxygen evolution catalyst (OEC) to improve the poor catalytic ability of BiV0.97Mo0.03O4 for water oxidation. The resulting BiV0.97Mo0.03O4/FeOOH photoanodes generated a significantly improved photocurrent for water oxidation compared to previous reported results, but the photocurrent of BiV0.97Mo0.03O4/FeOOH for water oxidation could not reach the photocurrent of BiV0.97Mo0.03O4 for sulfite oxidation. In order to examine the cause, the effects of Mo-doping on the interaction between BiVO4 and FeOOH and the effects of FeOOH on the electron–hole separation yield of BiV0.97Mo0.03O4 were investigated in detail, which provided new insights into semiconductor–OEC interactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...