The synthesis and characterization of Ag–N dual-doped p-type ZnO: experiment and theory
Abstract
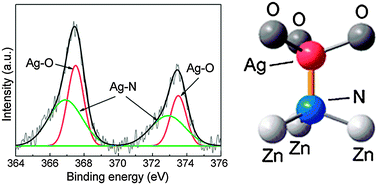
Ag–N dual-doped ZnO films have been fabricated by a chemical bath deposition method. The p-type conductivity of the dual-doped ZnO:(Ag, N) is stable over a long period of time, and the hole concentration in the ZnO:(Ag, N) is much higher than that in mono-doped ZnO:Ag or ZnO:N. We found that this is because AgZn–NO complex acceptors can be formed in ZnO:(Ag, N). First-principles calculations show that the complex acceptors generate a fully occupied band above the valance band maximum, so the acceptor levels become shallower and the hole concentration is increased. Furthermore, the binding energy of the Ag–N complex in ZnO is negative, so ZnO:(Ag, N) can be stable. These results indicate that the Ag–N dual-doping may be expected to be a potential route to achieving high-quality p-type ZnO for use in a variety of devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...