A new 3D four-fold interpenetrated dia-like polymer: gas sorption and computational analyses†
Abstract
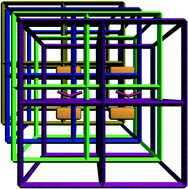
A new metal–organic framework, namely, {[Cu(bib)2]·NO3·4H2O}n (1) (bib = 2,3-bis(4-pyridyl)butane), was synthesized and characterized. In the structure of 1, nitrogen atoms of four bib ligands bind to the tetrahedrally coordinated metal ion. The bib ligands act as linear bidentate linkers to form a four-fold interpenetrated 3D framework with a dia-like topology. The H2 uptake of the dehydrated coordination framework of 1 was estimated using a computational method based on Connolly's algorithm, which indicated that adsorbed H2 is predominantly located around the outer surface of the pore through multipoint interactions with the inner surface of dehydrated 1′. The material has no significant adsorption for CO2 or N2 gas upon desolvation by long-time thermal activation, indicating that access to the void space is blocked by the large and immobile anions. The luminescence properties of sample 1 and dehydrated sample 1′ were also explored.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...