Formation of organic molecular nanocrystals under rigid confinement with analysis by solid state NMR†
Abstract
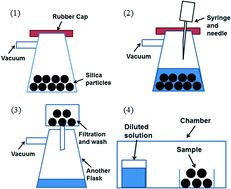
Crystallization in rigid confinement is a promising method to obtain organic molecular nanocrystals. However, the crystallization behavior and the related characterization methods are not well studied. Here we present a systematic study of the nucleation of organic molecular nanocrystals in rigid pores. Four different compounds were studied, ibuprofen, fenofibrate, griseofulvin and indomethacin, which range from simple to complex molecules. Solid-state Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) was employed to analyse the structure of these compounds inside pores which are difficult to characterize by other analytical methods. We successfully demonstrated the production of nano-crystalline ibuprofen, fenofibrate and griseofulvin in porous silica particles with ~40 nm pores. These nanocrystals showed significant enhancement in dissolution rates. These results help advance the fundamental understanding of nucleation under rigid confinement and may lead to potential applications in developing new formulations in the pharmaceutical industry.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...