The mechanism of blue photoluminescence from carbon nanodots
Abstract
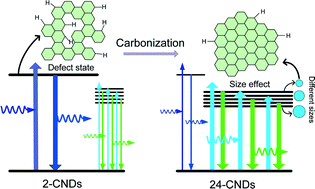
The blue photoluminescence from carbon nanodots (CNDs) weakens gradually and the most intense peak red-shifts slightly as the hydrothermal reaction time increases. The 890 cm−1 infrared vibration band, which is associated with carbon defects, decreases with the reaction time being consistent with the blue emission tendency. Based on the growth model of CNDs and understanding of photoluminescence from other carbon nanomaterials, carbon defects are believed to be responsible for the blue emission.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...