Synthesis, structures and luminescent properties of lanthanide coordination polymers involving biphenyl-3,4′,5-tricarboxylate†
Abstract
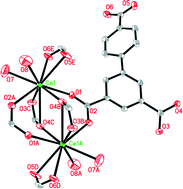
Based on biphenyl-3,4′,5-tricarboxylate (H3BPT), a series of lanthanide coordination polymers (CPs) formulated as {[Ln2(BPT)2(DMF)(H2O)3]·2DMF·3H2O}n [Ln = Ce (1), Pr (2) and Eu (3); DMF = N,N-dimethylformamide], {[Ln2(BPT)2(DMA)2(H2O)3]·0.5DMA·2.5H2O}n [Ln = La (4), Sm (5), Eu (6) and Tb (7); DMA = N,N-dimethylacetamide] and {[Ln(BPT)(DMSO)2]·H2O}n [Ln = Sm (8) and Nd (9); DMSO = dimethyl sulfoxide] have been synthesized and characterized. Compounds 1–3 are isostructural, and all of them exhibit three-dimensional networks with one-dimensional (1D) pear-shaped channels along the crystallographic a-axis and 1D rectangular channels along the crystallographic c-axis filled with free and coordinated solvents. Compounds 4–7 are isostructural, and each of the frameworks displays a 3D network exhibiting 1D channels filled with free and coordinated solvent molecules. Compounds 8–9 are isostructural and their structures are similar to those of 1–3 except for the different lanthanide ions and coordinated solvents. Structure analysis reveals that the net of 1–3 and 8–9 is a 3,6-connected net with the point symbol of (42·6)2(44·62·87·102), a subnet of flu net, while the net of 4–7 is a 3,3,6,6-connected net with the point symbol of (4·62)2(42·66·85·102)(42·62)(44·65·85·10). Luminescent measurements showed that compounds 3, 6, 7 and 9 exhibit the characteristic emission bands for the corresponding Ln(III) ions, while the emission spectra of 5 and 8 are mainly dominated by ligand-based emission.
- This article is part of the themed collection: International Year of Crystallography Celebration: Asia-Pacific

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...