Epitaxial growth of high quality AlN films on metallic aluminum substrates
Abstract
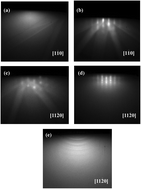
AlN (0001) epitaxial films have been grown on Al (111) substrates with an in-plane epitaxial relationship of AlN[11![[2 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0304.gif) 0]//Al[1
0]//Al[1![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0] by pulsed laser deposition. The as-grown AlN films grown at 450 °C exhibited a very smooth and flat surface with a surface root-mean-square roughness less than 1.1 nm. There is no interfacial layer existing between AlN films and Al substrates, indicating an abrupt interface. The as-grown ~302 nm thick AlN films are almost fully relaxed only with an in-plane compressive strain of 0.16%. With the increase in growth temperature, the interfacial layer thickness increases, resulting in the degradation in the crystalline quality of the as-grown AlN films. These AlN films are of great interest for the commercial development of AlN-based devices.
0] by pulsed laser deposition. The as-grown AlN films grown at 450 °C exhibited a very smooth and flat surface with a surface root-mean-square roughness less than 1.1 nm. There is no interfacial layer existing between AlN films and Al substrates, indicating an abrupt interface. The as-grown ~302 nm thick AlN films are almost fully relaxed only with an in-plane compressive strain of 0.16%. With the increase in growth temperature, the interfacial layer thickness increases, resulting in the degradation in the crystalline quality of the as-grown AlN films. These AlN films are of great interest for the commercial development of AlN-based devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...