Rapid interrogation of the physical and chemical characteristics of salbutamol sulphate aerosol from a pressurised metered-dose inhaler (pMDI)†
Abstract
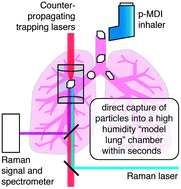
Individual micron-sized solid particles from a Salamol® pharmaceutical inhaler are stably captured in air using an optical trap for the first time. Raman spectroscopy of the levitated particles allows online interrogation of composition and deliquescent phase change within a high humidity environment that mimics the particle's travel from inhaler to lung.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...