Extraordinarily high pseudocapacitance of metal organic framework derived nanostructured cerium oxide†
Abstract
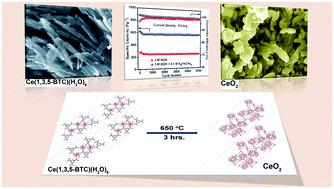
MOF derived CeO2 showed a pseudocapacitance of 1204 F g−1 at 0.2 A g−1, far exceeding its theoretical capacitance (560 F g−1). The present study demonstrates that combination of a two-way strategy, controlled nano-architecture and redox active electrolyte additive, could potentially alleviate both low energy density and capacitance fading issues plaguing the current metal oxide pseudocapacitors.
- This article is part of the themed collection: ChemComm 60th Anniversary Historic Papers from India

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...