Ultrafast electron injection at the cationic porphyrin–graphene interface assisted by molecular flattening†
Abstract
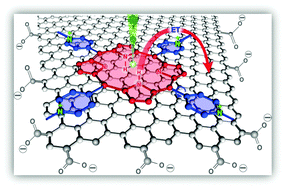
The steady-state and femtosecond (fs) time-resolved data clearly demonstrate that the charge transfer (CT) process at the porphyrin–graphene carboxylate (GC) interfaces can be tuned from zero to very sufficient and ultrafast by changing the electronic structure of the meso unit and the redox properties of the porphyrin cavity.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...