Electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution using amorphous tungsten phosphide nanoparticles†
Abstract
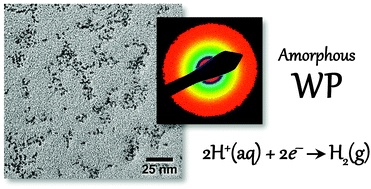
Amorphous tungsten phosphide (WP), which has been synthesized as colloidal nanoparticles with an average diameter of 3 nm, has been identified as a new electrocatalyst for the hydrogen-evolution reaction (HER) in acidic aqueous solutions. WP/Ti electrodes produced current densities of −10 mA cm−2 and −20 mA cm−2 at overpotentials of only −120 mV and −140 mV, respectively, in 0.50 M H2SO4(aq).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...