Ethylene bis-imidazoles are highly potent and selective activators for isozymes VA and VII of carbonic anhydrase, with a potential nootropic effect†
Abstract
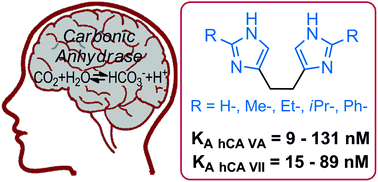
A series of ethylene bis-imidazoles was synthesized via a novel microwave-mediated synthesis. Biological testing on eight isozymes of carbonic anhydrase (CA) present in the human brain revealed compounds with nanomolar potency against CA VA and CA VII, also displaying excellent selectivity against other CA isozymes present in this organ.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...