Oxidation of allylic and benzylic alcohols to aldehydes and carboxylic acids†
Abstract
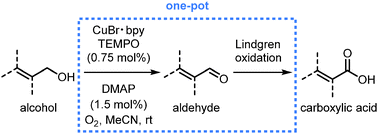
An oxidation of allylic and benzylic alcohols to the corresponding carboxylic acids is effected by merging a Cu-catalyzed oxidation using O2 as a terminal oxidant with a subsequent chlorite oxidation (Lindgren oxidation). The protocol was optimized to obtain pure products without chromatography or crystallization. Interception at the aldehyde stage allowed for Z/E-isomerization, thus rendering the oxidation stereoconvergent with respect to the configuration of the starting material.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...