Programmable drug release using bioresponsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for site-specific oral drug delivery†
Abstract
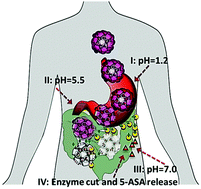
Novel mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) responsive to multiple biological stimuli (pH and enzymes) were prepared through conjugation with a structure modified soy protein isolate. The particles show an extremely high pro-drug (sulfasalazine) loading with programmable drug release in simulated gastrointestinal fluid.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...