Alkyne aminohalogenation enabled by DBU-activated N-haloimides: direct synthesis of halogenated enamines†
Abstract
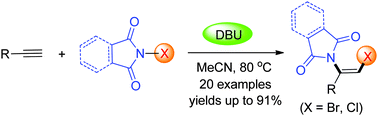
Activated by DBU, N-haloimides can be used as both halogen and nitrogen sources to achieve the difunctionalization of terminal alkynes, giving rise to useful halogenated enamines with high efficiency and high regio- and stereoselectivities. The cascade reaction features simple manipulation, mild conditions, a broad substrate scope, readily available reagents, and atom-economy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...