Abstract
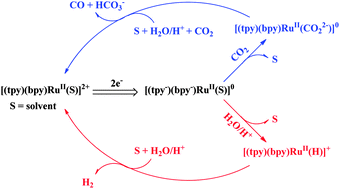
Electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide and of water/weak acids to hydrogen by a class of polypyridyl ruthenium complexes both occur by well-defined mechanisms involving common intermediates. Based on available mechanistic insight, conditions have been found for competitive electrocatalytic reduction of CO2–H2O–H2PO4− mixtures by a single metal complex catalyst to give syngas products with the H2 : CO ratio controllable by controlling the composition of the solutions.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Metal-Mediated Transformations of Small Molecules

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...