Covalent attachment of multilayers (CAM): a platform for pH switchable antimicrobial and anticoagulant polymeric surfaces†
Abstract
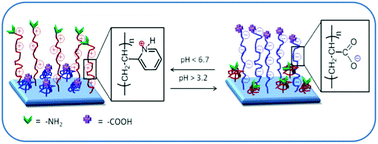
These studies show covalent attachment of multilayers (CAM) to chemically alter surfaces to achieve pH switchable antimicrobial and anticoagulant properties. Polyethylene (PE), poly(tetrafluoroethylene) (PTFE), and silicon (Si) surfaces were functionalized by tethering pH-responsive “switching” polyelectrolytes consisting of poly(2-vinyl pyridine) (P2VP) and poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) terminated with NH2 and COOH groups, respectively. At pH < 2.3, the P2VP segments are protonated and expended, but at pH > 5.5, they collapse while the PAA segments are expanded. The presence of terminal NH2 or COOH moieties on P2VP and PAA, respectively, facilitated the opportunity for covalently bonding ampicillin (AMP) and heparin (HEP) to both polyelectrolyte chains. Such surfaces, when exposed to S. aureus, inhibit the growth of microbial films (AMP) as well as anticoagulant properties (HEP). Comparison of “dynamic” pH dependent surfaces developed in these studies with “static” surfaces terminated with (AMP) entities shows significant enhancement in the longevity of surface activity against microbial film formation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...