A highly sensitive electrochemical sensor based on gold nanoparticles/multiwall carbon nanotubes-modified glassy carbon electrode for selective determination of traces of atenolol
Abstract
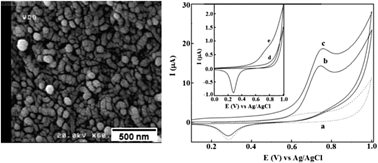
In the present study, the electrochemical oxidation of atenolol (ATN) at gold nanoparticles (GNPs)/multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs)-modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was studied using cyclic voltammetry, differential pulse voltammetry and chronoamperometry. The synergetic effects of GNPs and MWCNTs highly improved electrochemical response and sensitivity of the sensor. The effect of experimental parameters, including amount of MWCNTs, GNPs, electrodeposition time, solution pH and scan rate on the sensor response, was evaluated. Under optimum experimental conditions, the respective linear calibration range, detection limit and sensitivity of the sensor were obtained as 1–60 μM, 0.5 μM and 350 nA μM−1 for differential pulse voltammetry and 0.1–1 μM, 59 nM and 4.405 μA μM−1 for chronoamperometry. The proposed sensor was successfully applied to the determination of atenolol in pharmaceutical samples, human urine and blood serum as real samples. The method was also applied to monitor ATN in urine samples of a dosage-received volunteer. Satisfactory recoveries of analyte from samples clearly revealed that the proposed sensor is well applicable to clinical analysis, quality control and a routine determination of drugs in pharmaceutical formulations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...