An imprinted electrochemical sensor for bisphenol A determination based on electrodeposition of a graphene and Ag nanoparticle modified carbon electrode†
Abstract
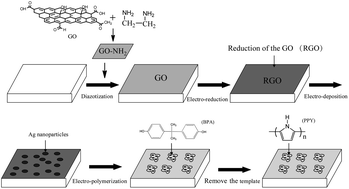
In this study, a highly sensitive and selective imprinted electrochemical sensor based on a Ag nanoparticle and graphene modified carbon electrode with covalent anchoring and electrochemical reduction was prepared for the determination of bisphenol A (BPA) in aqueous solution. The imprinted film was fabricated by electrodepositing pyrrole in the presence of BPA onto the graphene and Ag nanoparticle modified electrode surface. The morphologies of the electrodes were characterized by scanning electron microscopy. The electrochemical performance of the imprinted electrochemical sensor was investigated by cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry techniques in detail. The response currents of the imprinted electrochemical sensor exhibit a linear relationship toward the negative logarithm of the concentrations of BPA ranging from 1.0 × 10−11 to 1.0 × 10−8 mol L−1. The detection limit of the imprinted electrochemical sensor toward BPA is calculated to be 3.2 × 10−12 mol L−1 (S/N = 3). The imprinted electrochemical sensor was successfully applied to detect BPA in real plastic samples with good recoveries ranging from 93.3–103.0%.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...