Determination of trace rutin based on the surface plasmon resonance absorption of silver nanoparticles
Abstract
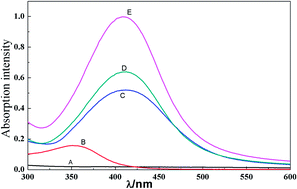
A simple method for the detection of rutin is proposed based on the surface plasmon resonance absorption of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) that derived from modified silver mirror reaction. AgNPs were produced from the reduction of silver ammonia in the circumstance of sodium hydroxide and ammonia at room temperature, due to the reducibility of phenol group in rutin. As the formation of AgNPs by this method does not need AgNPs seeds, color changes could be observed from the colorless rutin to the yellowish of AgNPs, resulting in a strong absorption signal at 410 nm. The formed AgNPs were nearly of the same size and the average dimension was about 2.5 nm (RSD 1.05%) by doing the statistics in transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image. It was found that the absorption intensities were proportional to rutin concentrations within the range of 0.50–10.0 μg mL−1, with detection limit of 0.16 μg mL−1. Finally, the present approach was successfully applied to detect rutin in the rutin tablet.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...