Microwave assisted extraction of ketamine and its metabolites from skeletal tissues
Abstract
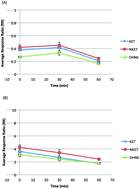
The use of Microwave Assisted Extraction (MAE) to extract ketamine and its metabolites from decomposed bone tissue is described. Wistar rats received 75 mg kg−1 (i.p.) ketamine (n = 12) or remained drug-free (controls, n = 4). Following euthanasia, rats were allowed to decompose to skeleton outdoors. Bones (vertebrae, rib, pelvi, femora, tibiae, humeri and scapulae) were collected and pooled. Analyte stability to MAE in methanol or acetone–hexane mixture (1 : 1, v/v) in a closed vessel microwave system was assessed, and acetone–hexane was chosen as the MAE solvent. Bone samples underwent MAE, and extracts were assayed using microplate solid phase extraction (MPSPE) in a mixed-mode configuration and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Drug levels, expressed as mass normalized response ratios, were used to characterize extraction time and the effect of MAE solvent volume on the extraction time and relative recovery for each analyte. Extraction time varied slightly with solvent volume, while relative analyte recovery did not differ significantly. Recovery was at least 90% of maximal value within the first 5 min for all samples examined and maximum recovery occurred within 20 minutes. MAE in combination with MPSPE offers a substantial improvement in analytical throughput for toxicological analysis of skeletal remains.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...