Acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation analysis using only high performance liquid chromatography
Abstract
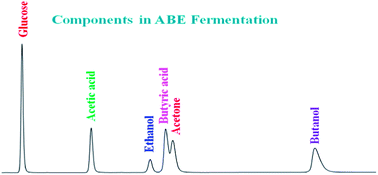
Currently, sample analysis of Acetone-butanol-ethanol (ABE) fermentation in Clostridium acetobutylicum is performed through the simultaneous use of both High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Gas Chromatography (GC). In this study, a novel method was developed for the quantification of substrate (glucose) and products (acetic acid, ethanol, butyric acid, acetone, and butanol) of ABE fermentation using only HPLC. The most favorable characterization of peaks of tested compounds were observed in a refractive index (RI) detector maintaining a flow rate of 0.5 ml min−1 with a column temperature of 30 °C. However, an overlap between butyric acid and acetone peaks was detected, and therefore a methodology was developed accounting for respective peak heights for the quantification of these compounds. During validation of the method, linear regression analysis of the calibration plot illustrated that there was a good linear relationship (correlation coefficient R2 > 0.9981) between peak area and concentration in the range of 0.31–5.0 mg ml−1. The quantitative recoveries of tested components were very close in range, 97.99–103.46%, and Relative Standard Deviation (RSD) values were lower than 4.90%. The results of statistical analysis proved that the method is precise, repeatable, reproducible, accurate, and sensitive, and hence can be employed for the quantification of components involved in ABE fermentation. This method was also used to quantify the products and substrates of fermentation samples using individual glucose and a combination of sugars.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...