Rapid identification of synthetic colorants in food samples by using indium oxide nanoparticle-functionalized porous polymer monolith coupled with HPLC-MS/MS
Abstract
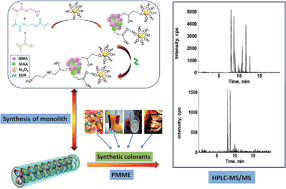
A synthetic protocol for the preparation of an indium oxide nanoparticle-functionalized poly(methacrylic acid-glycidyl methacrylate-ethylene dimethacrylate-ethanediamine) monolithic column is reported. Various techniques, including scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and thermal gravimetric analysis-derivative thermogravimetric analysis were employed to characterize the synthesized monolith. The modified monolithic column was coupled with high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) for determining synthetic colorants in various food samples. Under optimized conditions, good linearity was obtained for all the targets with squared regression coefficients greater than 0.9982. The limits of detection (S/N = 3) for 12 synthetic colorants were in the range of 0.012–2.97 μg kg−1. The intra-day and inter-day relative standard deviations, ranging from 2.7% to 8.5%, were within the acceptable range. The developed method was successfully applied to the determination of synthetic colorants in food samples (candy, milk, jelly, jam, canned food, juice, and carbonated drink). Target recoveries at different spiked levels ranged from 73.5% to 112.1% with relative standard deviations of less than 10.3%.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...