A three-dimensional interpenetrating electrode of reduced graphene oxide for selective detection of dopamine†
Abstract
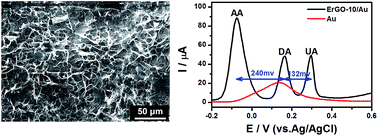
Electrochemical detection of dopamine plays an important role in medical diagnosis. In this paper, we report a three-dimensional (3D) interpenetrating graphene electrode fabricated by electrochemical reduction of graphene oxide for selective detection of dopamine. This electrochemically reduced graphene oxide (ErGO) electrode was used directly without further functionalization or blending with other functional materials. This electrode can efficiently lower the oxidation potential of ascorbic acid; thus, it is able to selectively detect dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid and uric acid. The ErGO-based biosensor exhibited a linear response towards dopamine in the concentration range of 0.1–10 μM with a low detection limit of 0.1 μM. Furthermore, this electrode has good reproducibility and environmental stability, and can be used to analyse real samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...