Sensitive and selective trypsin detection using redox cycling in the presence of l-ascorbic acid†
Abstract
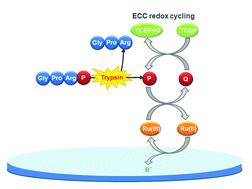
We report a simple, sensitive, and selective electrochemical method for trypsin detection that can cover a wide range of concentrations. The method is based on the proteolytic generation of an electroactive species (P) by trypsin followed by a signal-amplified electrochemical measurement of P using electrochemical–chemical (EC) or electrochemical–chemical–chemical (ECC) redox cycling. The detection is performed using bare indium-tin oxide (ITO) electrodes without washing steps. P is generated by the cleavage of an amide bond between P and oligopeptide (Gly-Pro-Arg) at the C-terminal of Gly-Pro-Arg-P. Four trypsin products including 4-amino-1-naphthol (AN) and their trypsin substrates are investigated to obtain a high signal-to-background ratio in ECC redox cycling. AN and its trypsin substrate produce the highest signal-to-background ratio. The detection limits obtained with ECC redox cycling involving AN (approximately 1 ng mL−1 and 100 ng mL−1 with an incubation period of 2 h and 30 min, respectively) in Tris buffer (pH 8.0) are lower than those obtained with EC redox cycling involving AN (approximately 5 ng mL−1 and 200 ng mL−1 with an incubation period of 2 h and 30 min, respectively). In trypsin detection using ECC redox cycling, the interference effects of electroactive species such as L-ascorbic acid and uric acid are not significant.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...