Voltammetric pH sensor based on an edge plane pyrolytic graphite electrode
Abstract
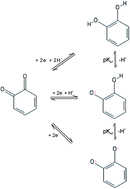
A simple sensor for pH determination is reported using unmodified edge plane pyrolytic graphite (EPPG) electrodes. The analysis is based on the electro-reduction of surface quinone groups on the EPPG which was characterised using cyclic voltammetry (CV) and optimised with square-wave voltammetry (SWV). Under optimised conditions, a linear response is observed between the peak potential and pH with a gradient of ∼59 mV per pH (at 25 °C), which corresponds well with Nernstian behaviour based on a 2 proton, 2 electron system over the aqueous pH range 1.0 to 13.0. As such, an EPPG is suggested as a reagent free and robust pH sensing material.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...