Cell specific electrodes for neuronal network reconstruction and monitoring
Abstract
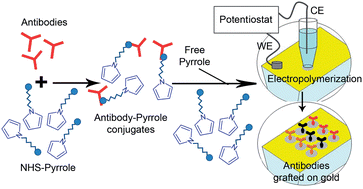
Direct interfacing of neurons with electronic devices has been investigated for both prosthetic and neuro-computing applications. In vitro neuronal networks provide great tools not only for improving neuroprostheses but also to take advantage of their computing abilities. However, it is often difficult to organize neuronal networks according to specific cell distributions. Our aim was to develop a cell-type specific immobilization of neurons on individual electrodes to produce organized in vitro neuronal networks on multi-electrode arrays (MEAs). We demonstrate the selective capture of retinal neurons on antibody functionalized surfaces following the formation of self-assembled monolayers from protein–thiol conjugates by simple contact and protein–polypyrrole deposits by electrochemical functionalization. This neuronal selection was achieved on gold for either cone photoreceptors or retinal ganglion neurons using a PNA lectin or a Thy1 antibody, respectively. Anti-fouling of un-functionalized gold surfaces was optimized to increase the capture efficiencies. The technique was extended to electrode arrays by addressing electropolymerization of pyrrole monomers and pyrrole–protein conjugates to active electrodes. Retinal ganglion cell recording on the array further demonstrated the integrity of these neurons following their selection on polypyrrole-coated electrodes. Therefore, this protein–polypyrrole electrodeposition could provide a new approach to generate organized in vitro neuronal networks.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Probe and chip approaches to cell analysis

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...