Advances in nanowire transistors for biological analysis and cellular investigation
Abstract
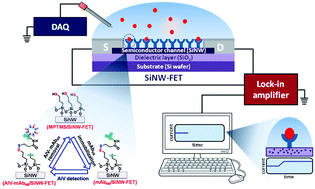
Electrical biosensors based on silicon nanowire field-effect transistors (SiNW-FETs) have attracted enormous interest in the biosensing field. SiNW-FETs have proven to be significant and efficient in detecting diverse biomolecular species with the advantages of high probing sensitivity, target selectivity, real-time recording and label-free detection. In recent years, significant advances in biosensors have been achieved, particularly for cellular investigation and biomedical diagnosis. In this critical review, we will report on the latest developments in biosensing with SiNW-FETs and discuss recent advancements in the innovative designs of SiNW-FET devices. This critical review introduces the basic instrumental setup and working principle of SiNW-FETs. Technical approaches that attempted to enhance the detection sensitivity and target selectivity of SiNW-FET sensors are discussed. In terms of applications, we review the recent achievements with SiNW-FET biosensors for the investigations of protein–protein interaction, DNA/RNA/PNA hybridization, virus detection, cellular recording, biological kinetics, and clinical diagnosis. In addition, the novel architecture designs of the SiNW-FET devices are highlighted in studies of live neuron cells, electrophysiological measurements and other signal transduction pathways. Despite these remarkable achievements, certain improvements remain necessary in the device performance and clinical applications of FET-based biosensors; thus, several prospects about the future development of nanowire transistor-based instruments for biosensing employments are discussed at the end of this review.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...