Aqueous electrolyte-gated ZnO transistors for environmental and biological sensing†
Abstract
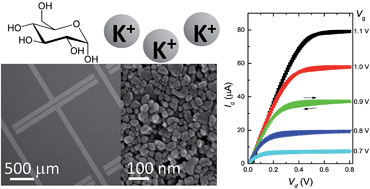
Electrolyte-gated transistors (EGTs) based on ZnO thin films, obtained by solution processing of suspensions of nanoparticles, have a low turn-on voltage (<0.5 V), a high on/off ratio and transconductance exceeding 0.2 mS. Importantly, the ZnO surface can be functionalized with a large variety of molecular recognition elements, making these devices ideal transducers in physiological and environmental monitoring. We present simple glucose-sensing and ion-selective EGTs, demonstrating the versatility of such devices in biosensing.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...