Perylene derivative-bridged Au–graphene nanohybrid for label-free HpDNA biosensor†
Abstract
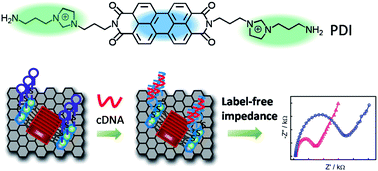
Along with the challenges of wet-chemically preparing graphene-based nanohybrids, for example easy aggregation, low-stability in solution environment and insufficient loading amount, here we report the preparation and application of a type of π-conjugated molecule, perylenetetracarboxylic acid di-imide (PDI)-functionalized graphene material with high density of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). In this nanohybrid, the PDI molecule comprises five-connected benzene rings and positively charged terminals composed of two symmetrical imidazole rings and amine groups, which offers the intrinsic driving force for π–π interactions with graphene and also serves as the active sites for immobilization of AuNPs. Transmission electron microscopy results demonstrated that AuNPs were uniformly dispersed and densely covered the PDI-functionalized graphene compared to the control experiment without PDI. To prove its biological application, the Au–PDI–graphene nanohybrid was chosen as a sensing material for fabricating a label-free electrochemical impedance hairpin DNA (hpDNA) biosensor for detection of human immunodeficiency virus 1 gene. When hpDNA was hybridized, it exhibited a sensitive electrochemical impedance variation on an Au–PDI–graphene modified electrode. This fabricated hpDNA biosensor reveals a wide linear detection range and a relatively low detection limit. Thanks to its high stability and efficient electrochemical impedance sensitivity, this nanohybrid would offer a broad range of possible DNA sequences for specific applications in biodiagnostics and bionanotechnology.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...