Durable gels with ultra-low adhesion to ice†
Abstract
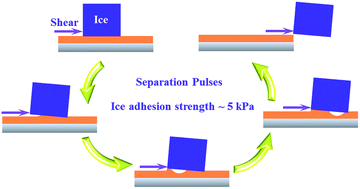
In this work, building on the principles of adhesion mechanics, we developed novel inexpensive, environmentally benign, non-corrosive PDMS gels that offer ultra-low adhesion to ice as well as outstanding mechanical durability. We elucidated the mechanism of separation of ice from our PDMS gels via separation pulses. We envision that our durable PDMS gels with ultra-low ice adhesion strength as well as the improved understanding of the separation mechanism will enable universal deicing design strategies in aviation, maritime, power, automotive, and energy sectors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...