Interface layer formation in solid polymer electrolyte lithium batteries: an XPS study†
Abstract
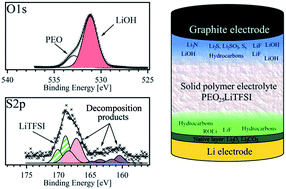
The first characterization studies of the interface layer formed between a Li-ion battery electrode and a solid polymer electrolyte (SPE) are presented here. SPEs are well known for their electrochemical stability and excellent safety, and thus considered good alternatives to conventional liquid/gel electrolytes in high-energy density battery devices. This work comprises studies of solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation in SPE-based graphite|Li cells using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). SPEs based on high molecular weight poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) and lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI) salt are studied. Large amounts of LiOH are observed, and the XPS results indicate a correlation with moisture contamination in the SPEs. The water contents are quantitatively determined to be in the range of hundreds of ppm in the pure PEO as well as in the polymer electrolytes, which are prepared by a conventional SPE preparation method using different batches of PEO and at different drying temperatures. Moreover, severe salt degradation is observed at the graphite–SPE interface after the 1st discharge, while the salt is found to be more stable at the Li–SPE interface or when using LiTFSI-based liquid electrolyte equivalents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...