Responsive aqueous foams stabilised by silica nanoparticles hydrophobised in situ with a switchable surfactant†
Abstract
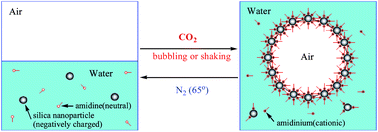
In the recent past there has been a growing interest in switchable surfactants and stimuli-responsive surface-active particles, since both have surface activity which is either switchable or controllable and they can be recovered and re-used afterwards. Among various triggers the CO2/N2 trigger is particularly environmentally benign. In this paper a facile protocol to obtain switchable surface-active silica nanoparticles using a CO2/N2 trigger is proposed and their utilization in producing responsive aqueous foams with the same trigger is examined. Using a switchable surfactant, N′-dodecyl-N,N-dimethylacetamidinium bicarbonate, which can be switched between a cationic surfactant and a surface-inactive neutral form by bubbling with CO2 and N2 respectively, bare silica nanoparticles can be hydrophobised in situ to become surface-active nanoparticles and the switch of the surfactant can thus be transferred to the particles. Thus responsive particle-stabilised aqueous foams can be prepared. Compared with foams stabilised by specially synthesized switchable or stimuli-responsive particles, the method reported here is much easier, whereas compared with those stabilised by switchable or stimuli-responsive surfactants the method here requires a relatively low concentration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...