Natural rubber for sustainable high-power electrical energy generation†
Abstract
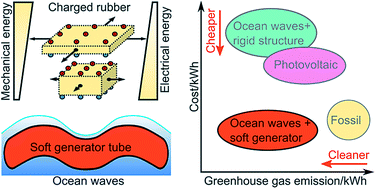
Clean, renewable and abundant sources of energy, such as the vast energy of ocean waves, are untapped today, because no technology exists to convert such mechanical motions to electricity economically. Other sources of mechanical energy, such as motions of people and vibrations of buildings and bridges, can potentially power portable electronics and distributed sensors. Here we show that natural rubber can be used to construct generators of high performance and low cost. Natural rubber has higher elastic modulus, fracture energy and dielectric strength than a commonly studied acrylic elastomer. We demonstrate high energy densities (369 mJ g−1) and high power densities (200 mW g−1), and estimate low levelized cost of electricity (5–11 ct kW−1 h−1). Soft generators based on natural rubber enable clean, low-cost, large-scale generation of electricity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...