Structural evaluation and catalytic performance of nano-Au supported on nanocrystalline Ce0.9Fe0.1O2−δ solid solution for oxidation of carbon monoxide and benzylamine†
Abstract
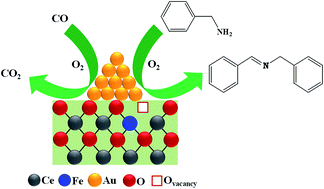
In this work, we systematically investigated the structure–activity performance of nanosized Au/CeO2 and Au/Ce0.9Fe0.1O2−δ catalysts, along with nanocrystalline CeO2 and Ce0.9Fe0.1O2−δ supports, for the oxidation of carbon monoxide and benzylamine. An extensive physicochemical characterization was undertaken using XRD, BET surface area, BJH analysis, TG-DTA, XPS, TEM, Raman, AAS and CHN analyses. XRD studies confirmed the formation of smaller sized Ce0.9Fe0.1O2−δ nanocrystallites due to the incorporation of Fe3+ ions into the CeO2 lattice. Interestingly, Raman analysis revealed that the addition of Au remarkably improves the structural properties of the supports, evidenced by F2g peak shift and peak broadening, a significant observation in the present work. TEM images revealed the formation of smaller Au particles for Au/Ce0.9Fe0.1O2−δ (∼3.6 nm) compared with Au/CeO2 (∼5.3 nm), attributed to ample oxygen vacancies present on the Ce0.9Fe0.1O2−δ surface. XPS studies indicated that Au and Fe are present in metallic and +3 oxidation states, respectively, whereas Ce is present in both +4 and +3 oxidation states (confirming its redox nature). Activity results showed that the incorporation of Fe outstandingly enhances the efficacy of the Au/CeO2 catalyst for both CO oxidation and benzylamine oxidation. A 50% CO conversion was achieved at ∼349 and 330 K for Au/CeO2 and Au/Ce0.9Fe0.1O2−δ catalysts, respectively. As well, the Au/Ce0.9Fe0.1O2−δ catalyst showed ∼99% benzylamine conversion with ∼100% dibenzylimine selectivity for 7 h reaction time and 403 K temperature, whereas only 81% benzylamine conversion was achieved for the Au/CeO2 sample under similar conditions. The excellent performance of the Au/Ce0.9Fe0.1O2−δ catalyst is mainly due to the existence of smaller Au particles and an improved synergetic effect between the Au and the Ce0.9Fe0.1O2−δ support. It is confirmed that the oxidation efficiency of the Au catalysts is highly dependent on the preparation method.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...