In situ synthesis of metal/polymer nanocomposite thin films on glass substrates by using highly cross-linked polymer matrices with tailorable ion exchange capabilities†
Abstract
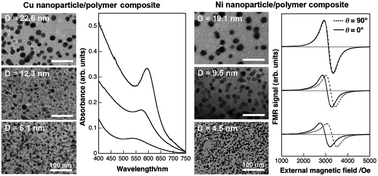
We describe the use of ion-exchangeable, highly cross-linked polymer films as a matrix for the synthesis of nanocomposite thin films and patterns with embedded Cu and Ni nanoparticles. We have successfully controlled the size of metal nanoparticles and thus optical and magnetic properties of the films by varying the initial amount of doped metal ions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...