Site-specific immobilization of microbes using carbon nanotubes and dielectrophoretic force for microfluidic applications†
Abstract
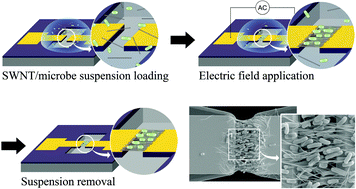
We developed a microbial immobilization method for successful applications in microfluidic devices. Single-walled nanotubes and Escherichia coli were aligned between two cantilever electrodes by a positive dielectrophoretic force resulting in a film of single-walled nanotubes with attached Escherichia coli. Because this film has a suspended and porous structure, it has a larger reaction area and higher reactant transfer efficiency than film attached to the substrate surface. The cell density of film was easily controlled by varying the cell concentration of the suspension and varying the electric field. The film showed excellent stability of enzyme activity, as demonstrated by measuring continuous reaction and long-term storage times using recombinant Escherichia coli that expressed organophosphorus hydrolase.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...