Poly(lactic acid) nanoparticles of the lead anticancer ruthenium compound KP1019 and its surfactant-mediated activation
Abstract
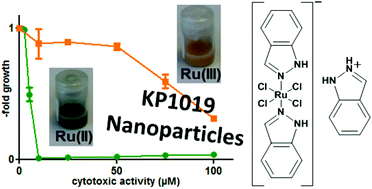
Nanoparticle formulations offer besides the advantage of passive drug targeting also the opportunity to increase the stability of drugs. KP1019 is a lead ruthenium(III) compound which has been successfully tested in a clinical phase I trial. However, it is characterized by low stability in aqueous solution especially at physiological pH. To overcome this limitation, poly(lactic acid) (PLA) nanoparticles of KP1019 with two different surfactants (Pluronic F68 and Tween 80) were prepared by a single oil-in-water (o/w) emulsion. Cytotoxicity measurements comparing different aged Tween 80 nanoparticles revealed that the color change from brown to green was associated with an up to 20 fold increased activity compared to “free” KP1019. Further investigations suggested that this is based on the formation of enhanced intracellular reactive oxygen species levels. Additional studies revealed that the origin of the green color is a reaction between KP1019 and Tween 80. Kinetic studies of this reaction mixture using UV-Vis, ESI-MS and ESR spectroscopy indicated on the one hand a coordination of Tween 80 to KP1019, and on the other hand, the color change was found to correlate with a reduction of the Ru(III) center by the surfactant. Together, the results provide a first experimental approach to stabilize a biologically active Ru(II) species of KP1019 in aqueous solution, which probably can be also used to selectively generate this activated species in the tumor tissue via delivery of KP1019 using Tween 80 nanoparticles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...