Water oxidation by manganese oxides formed from tetranuclear precursor complexes: the influence of phosphate on structure and activity†
Abstract
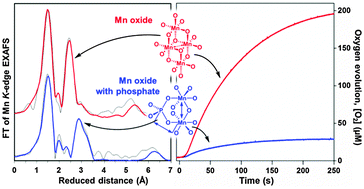
Two types of manganese oxides have been prepared by hydrolysis of tetranuclear Mn(III) complexes in the presence or absence of phosphate ions. The oxides have been characterized structurally using X-ray absorption spectroscopy and functionally by O2 evolution measurements. The structures of the oxides prepared in the absence of phosphate are dominated by di-μ-oxo bridged manganese ions that form layers with limited long-range order, consisting of edge-sharing MnO6 octahedra. The average manganese oxidation state is +3.5. The structure of these oxides is closely related to other manganese oxides reported as water oxidation catalysts. They show high oxygen evolution activity in a light-driven system containing [Ru(bpy)3]2+ and S2O82− at pH 7. In contrast, the oxides formed by hydrolysis in the presence of phosphate ions contain almost no di-μ-oxo bridged manganese ions. Instead the phosphate groups are acting as bridges between the manganese ions. The average oxidation state of manganese ions is +3. This type of oxide has much lower water oxidation activity in the light-driven system. Correlations between different structural motifs and the function as a water oxidation catalyst are discussed and the lower activity in the phosphate containing oxide is linked to the absence of protonable di-μ-oxo bridges.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Photosynthesis: From Natural to Artificial

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...