Theoretical prediction of carbon dioxide reduction to methane at coordinatively unsaturated ferric site in the presence of Cu impurities
Abstract
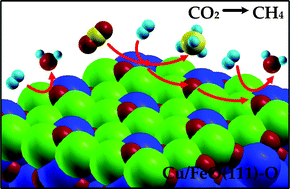
Based on first principles calculations, we have found that the reducibility of a polar FeO(111) surface can be improved by incorporating some Cu dopants. The resulting coordinatively unsaturated ferric site could effectively reduce carbon dioxide to methane in a H2 atmosphere.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...