Theoretical study on the peroxyl radicals scavenging activity of esculetin and its regeneration in aqueous solution†
Abstract
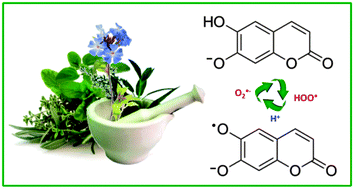
The study of the ˙OOH, ˙OOCH3 and ˙OOCHCH2 radicals scavenging processes by esculetin (ES) was carried out in aqueous and lipid media, using the density functional theory. Three reaction mechanisms were considered: single electron transfer (SET), hydrogen transfer (HT) and radical adduct formation (RAF). Rate constants and branching ratios for the different paths are reported. It was found that in lipid media the main mechanism of reaction is HT, while in aqueous solution it depends on the predominant acid–base form of esculetin. HT was found to be the main mechanism involved in the free radical scavenging activity of neutral esculetin (H2ES), while for anionic esculetin (HES−) the relative importance of the different mechanisms changes with the reacting radical. Based on the calculated rate constants, it is proposed that esculetin has moderate peroxyl scavenging activity in lipid media while in aqueous solution, at physiological pH, it is excellent for that purpose. In addition, the possible regeneration of ES, after scavenging the first radical, was investigated in aqueous solution, at physiological pH. It was found that regeneration is very likely to occur, which suggests that this compound has the ability to scavenge several radical equivalents (two per cycle), under such conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...