Core-excited and shape resonances of uracil†
Abstract
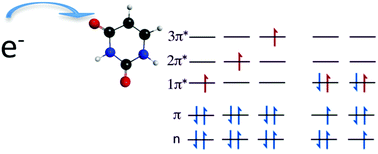
Attachment of an electron to nucleobases leads to metastable anion states called resonances. There are two types of electronic resonances present in the nucleobases. Shape resonances occur when the electron is attached to one of the previously unoccupied π* orbitals of the base. An electron can also be attached to an electronically excited state leading to core-excited or Feshbach resonances. In this work we present both types of resonances of uracil, a nucleobase present in RNA. Both the positions and widths of the resonances have been calculated using a stabilization method coupled with high level electronic structure methods. Core-excited resonances which are accessed with electrons of energy >4.6 eV are expected to play an important role in the dissociative electron attachment of uracil. Mixing between configurations corresponding to shape and core-excited resonances is also present which complicates the theoretical treatment of this system and necessitates multiconfigurational approaches for a proper description.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...