Tunable water desalination across graphene oxide framework membranes
Abstract
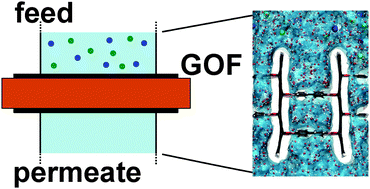
The performance of graphene oxide framework (GOF) membranes for water desalination is assessed using classical molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The coupling between water permeability and salt rejection of GOF membranes is studied as a function of linker concentration n, thickness h and applied pressure ΔP. The simulations reveal that water permeability in GOF-(n,h) membranes can be tuned from ∼5 (n = 32 and h = 6.5 nm) to 400 L cm−2 day−1 MPa−1 (n = 64 and h = 2.5 nm) and follows a Cnh−αn law. For a given pore size (n = 16 or 32), water permeability of GOF membranes increases when the pore spacing decreases, whereas for a given pore spacing (n = 32 or 64), water permeability increases by up to two orders of magnitude when the pore size increases. Furthermore, for linker concentrations n ≤ 32, the high water permeability corresponds to a 100% salt rejection, elevating this type of GOF membrane as an ideal candidate for water desalination. Compared to experimental performance of reverse osmosis membranes, our calculations suggest that under the same conditions of applied pressure and characteristics of membranes (ΔP ∼ 10 MPa and h ∼ 100 nm), one can expect a perfect salt rejection coupled to a water permeability two orders of magnitude higher than existing technologies, i.e., from a few cL cm−2 day−1 MPa−1 to a few L cm−2 day−1 MPa−1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...