Novel high-efficiency crystalline-silicon-based compound heterojunction solar cells: HCT (heterojunction with compound thin-layer)†
Abstract
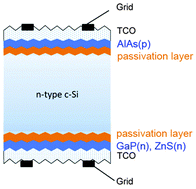
With an amorphous silicon (a-Si:H)/crystalline silicon (c-Si) heterojunction structure, the heterojunction with intrinsic thin-layer (HIT) solar cell has become one of the most promising technologies for c-Si based solar cells. By replacing a-Si:H thin films with appropriate compound semiconductors, we propose novel heterojunction structures which allow c-Si heterojunction solar cells to possess higher power conversion efficiencies than HIT solar cells. Several promising heterojunction candidates and hetero-structures have been proposed in this work, and this kind of novel c-Si compound heterojunction solar cell is denominated HCT (heterojunction with a compound thin-layer). The feasibilities of these novel HCT structures are further investigated by theoretical approaches, and the modeling results demonstrate the device performance improvement. Finally, this paper proclaims the compound selection standards and essentials of achieving high-efficiency HCT solar cells, which are guidelines for the real device implementation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...