Determining the storage, availability and reactivity of NH3 within Cu-Chabazite-based Ammonia Selective Catalytic Reduction systems†
Abstract
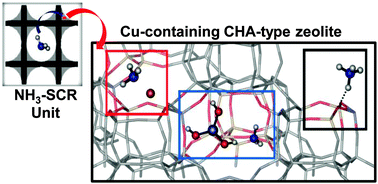
Three different types of NH3 species can be simultaneously present on Cu2+-exchanged CHA-type zeolites, commonly used in Ammonia Selective Catalytic Reduction (NH3-SCR) systems. These include ammonium ions (NH4+), formed on the Brønsted acid sites, [Cu(NH3)4]2+ complexes, resulting from NH3 coordination with the Cu2+ Lewis sites, and NH3 adsorbed on extra-framework Al (EFAl) species, in contrast to the only two reacting NH3 species recently reported on Cu-SSZ-13 zeolite. The NH4+ ions react very slowly in comparison to NH3 coordinated to Cu2+ ions and are likely to contribute little to the standard NH3-SCR process, with the Brønsted groups acting primarily as NH3 storage sites. The availability/reactivity of NH4+ ions can be however, notably improved by submitting the zeolite to repeated exchanges with Cu2+, accompanied by a remarkable enhancement in the low temperature activity. Moreover, the presence of EFAl species could also have a positive influence on the reaction rate of the available NH4+ ions. These results have important implications for NH3 storage and availability in Cu-Chabazite-based NH3-SCR systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...