Al–C hybrid nanoclustered anodes for lithium ion batteries with high electrical capacity and cyclic stability†
Abstract
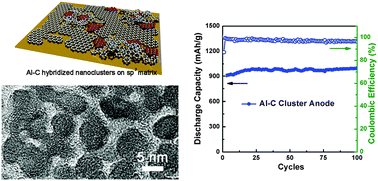
Structurally regulated and hybridized Al–C nanoclusters are prepared from C60 and Al precursors by thermal evaporation-combined plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition. The resulting Al–C hybrid nanoclustered anodes for Li-ion batteries exhibit a high reversible capacity of >900 mA h g−1 at an optimized current density of 6 A g−1 for over 100 cycles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...