Electrochemical evaluation of sarcomeric α-actinin in embryoid bodies after gene silencing using an LSI-based amperometric sensor array†
Abstract
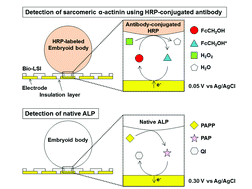
In the present study, gene analysis using siRNAs for cell differentiation of embryonic stem (ES) cells was performed using an LSI-based amperometric sensor array (Bio-LSI). CITED2 and WNT11 were silenced using siRNA, and then the effect of these genes on the differentiation of ES cells into cardiomyocytes was evaluated. For the evaluation, endogenous ALP activity and sarcomeric α-actinin were electrochemically detected using the Bio-LSI system. These results show the crucial role of these genes in determining the fate of differentiation of ES cells. These results also show that the Bio-LSI is a great tool for cell analysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...