Numerical and experimental investigation of NIR-to-visible energy up-conversion in Er3+-doped sol–gel SiO2 powders
Abstract
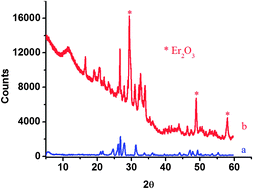
Er-doped SiO2 powders were prepared by a simple and straightforward sol–gel method using tetraethoxysilane and erbium triflate as sources of SiO2 and Er2O3. Excitation with near-infrared 800 and 980 nm light initiated an energy up-conversion process in these materials, which resulted in the emission in the predominantly red and green parts of the spectrum. Laser power dependence of the intensity of the up-converted emission was studied both experimentally and by using a numerical model to understand the up-conversion mechanism. Excited state absorption (ESA) and five unique ion–ion energy transfer up-conversion (ETU) processes between the relevant levels are identified as possible mechanisms for the observed luminescence. The efficient NIR-visible upconversion was observed even at comparatively low powers of 200 mW cm−2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...