Carbazole based polymers as hosts for blue iridium emitters: synthesis, photophysics and high efficiency PLEDs
Abstract
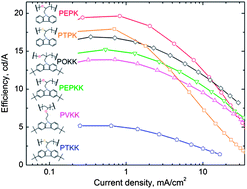
This article reports the synthesis of new carbazole based polymers and their application as hosts in sky-blue polymer light emitting devices (PLEDs) with a solution-processed emitting layer doped with a cyclometalated Ir(III) complex. We systematically investigate their effect on the PLED performance. A current efficiency of 19.7 cd A−1 and a brightness of 1850 cd m−2 were achieved with these polymers. The roll-off in electrophosphorescent quantum efficiency in PLEDs was shown to arise mainly from triplet–triplet annihilation between dopants in the hosts with tert-butyl groups. It has been shown that in the devices with hosts without tert-butyl groups the efficiency roll-off is additionally affected by electric field quenching. In these carbazole based polymers, triplet dimers are formed and tert-butyl groups do not limit the intermolecular interactions to prevent triplet dimer formation, nevertheless tert-butyl groups reduce charge transport.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...